IndAS 23 Borrowing Costs: It is quite common for an entity to borrow funds to meet its various business needs like the acquisition of the building, day-to-day operations, etc. On such borrowed funds an entity incurs the cost known as borrowing cost. Now, the query arises how such borrowing costs should be treated while preparing the financial statements?
Quick Links
IndAS 23 Borrowing Costs
The treatment of such borrowing cost is prescribed under Ind AS 23, AS 16 under IGAAP, and IAS 23 under IFRS. The objective of this article is to prescribe the treatment of borrowing costs as prescribed under Ind AS 23 along with highlighting the differences between AS 16 and IAS 23. Must Check Various Types of Lease.
Core Principle
- Borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or production of a qualifying asset form part of the cost of that asset.
- Other borrowing costs are recognized as an expense
⇑ Borrowing costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or production of a qualifying asset form part of the cost of that asset.
⇓Other borrowing costs are recognized as an expense.
A qualifying Asset is an asset that necessarily takes a substantial period of time to get ready for its intended use or sale.
Borrowing Cost definition
Borrowing costs are defined as interest and other costs that an entity incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds.
As Borrowing costs may include:
- (a) Interest expense calculated using the effective interest method as described in Ind AS 39 Financial Instruments.
- (b) Finance charges in respect of finance leases recognized in accordance with Ind AS 17 Leases; and
- (c) Exchange differences arising from foreign currency borrowings to the extent that they are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs. You may also like Contingent Liability.
Under IGAAP (AS 16) – there is no reference to the effective interest rate.
Scope
- This standard is applied in accounting for borrowing costs.
- It does not deal with the actual or imputed cost of equity, including preferred capital, which is not classified as a liability. For example: Dividends paid on equity shares, cost of issuance of equity, and cost on Irredeemable preference share capital will not be included as borrowing costs within the purview of this standard.
- This standard is not required to apply to borrowing costs directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or production of:
- Qualifying asset measured at fair value {For example A biological asset Ind AS 41}
- Inventories that are manufactured, or otherwise produced, in large quantities on a repetitive basis
Borrowing costs are interest and other costs that an entity incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds. It may include:
- interest expense calculated using the effective interest method as described in Ind AS 109, Financial Instruments;
- interest in respect of lease liabilities recognized in accordance with Ind AS 116, Leases; and
- exchange differences arising from foreign currency borrowings to the extent that they are regarded as an adjustment to interest costs.
Under IGAAP (AS 16) –Borrowing costs does not include any scope exemptions similar to Ind AS or IAS.
Exchange differences to be included in borrowing costs
With regard to the exchange difference required to be treated as borrowing costs in accordance with paragraph 6(e), the manner of arriving at the adjustments stated therein shall be as follows:
- (i) The adjustment should be of an amount that is equivalent to the extent to which the exchange loss does not exceed the difference between the cost of borrowing in functional currency when compared to the cost of borrowing in a foreign currency.
- (ii) where there is an unrealized exchange loss which is treated as an adjustment to interest and subsequently there is a realized or unrealized gain in respect of the settlement or translation of the same borrowing, the gain to the extent of the loss previously recognized as an adjustment should also be recognized as an adjustment to interest.
Under IAS 23 – The above guidance on how the adjustment prescribed in para 6(e) is to be determined is not found in IAS 23.
Treatment of Borrowing Cost
- 1) If the borrowing cost incurred is directly attributable to the acquisition, construction, or production of a qualifying asset, then it should be capitalized as part of the cost of the asset.
- 2) Otherwise it should be expensed in the profit or loss.
- 3) Note: In the case of a hyperinflationary economy, part of the borrowing cost that compensates for the inflation during the same period should be expensed in profit or loss.
Qualifying Assets
A qualifying asset is an asset that necessarily takes a substantial period of time to get ready for its intended use or sale.
Financial assets, and inventories that are manufactured, or otherwise produced, over a short period of time, are not qualifying assets. Assets that are ready for their intended use or sale when acquired are not qualifying assets. Must Read Weighted Average Cost of Capital.
Borrowing cost eligible for capitalization
Borrowing cost which is directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of a qualifying asset is capitalized. A borrowing cost is said to be directly attributable if it can be avoided when the expenditure on a qualifying asset is not made.
Specific borrowing
When an entity borrows funds specifically for the purpose of obtaining a particular qualifying asset, the borrowing costs that directly relate to that qualifying asset can be readily identified.
The amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalization is the actual borrowing costs incurred on those funds during the period reduced by any investment income earned on the temporary investment of idle funds.
General borrowing
In the case of general borrowings, it may be difficult to identify a direct relationship between particular borrowings and a qualifying asset and to determine the borrowings that could otherwise have been avoided.
Rate of Capitalisation
Total general borrowing cost for the period / Weighted average total general borrowings
Expenditure to which the capitalization rate is applied:-
| Particular | Amount |
| Opening balance of Qualifying Asset (Including borrowing cost previously capitalised) | XXX |
| Add: Cash expenditure incurred | XXX |
| Add: Transfer or consumption of other assets and material | XXX |
| Add: Assumption of Interest bearing liabilities | XXX |
| Less: Progress payments received | XXX |
| Less: Pre-Sale Deposit | XXX |
Note: The amount of borrowing cost eligible to capitalize should not exceed the actual borrowing cost in case of general borrowing.
Period of capitalisation (Commencement of capitalisation)
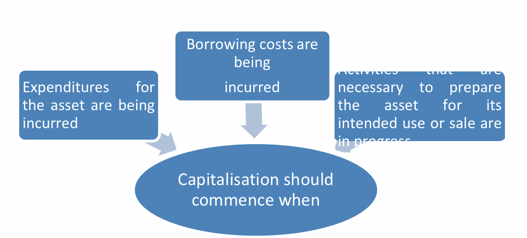
Suspension of capitalisation
- Capitalization should be suspended in the extended periods during which active development of qualifying assets is interrupted.
- Active development interruption means development not taking place due to abnormal reasons
Cessation of capitalisation
Capitalization should cease when
- Substantially all the activities necessary to prepare the qualifying asset for its intended use or sale are complete.
- Borrowing costs are not being incurred.
Other Key Points:– Recognition of an Impairment Loss: when the carrying amount or expected cost of a qualifying asset exceeds its recoverable amount or N.R.V., the carrying amount is written down or written off in accordance with the requirement of relevant standards IND AS 36 or 2. Must Check Supply Chain Management.
Disclosure
- a) Amount of borrowing cost capitalized during the period.
- b) Capitalisation rate used.
Author -CA. Pankaj Sharma
Release of Educational Material on Ind AS 23, Borrowing Costs – (27-01-2024)
Recommended

