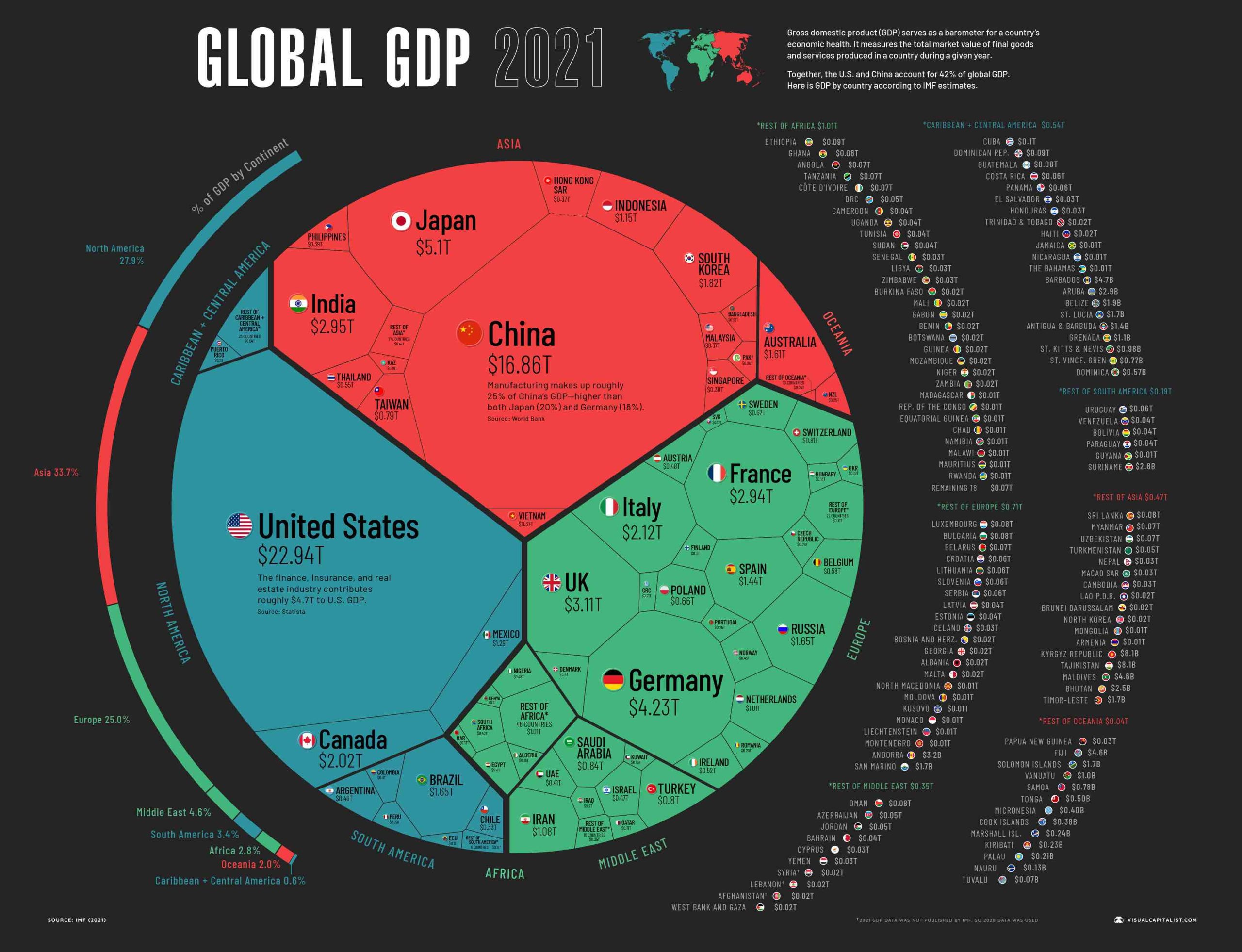
GDP of India: India becomes the 6th largest economy in the world, climbing two places to overtake Britain and France. GDP, i.e., the Gross Domestic Product – means the total sum of goods and services in the country, which can be counted in money, which is a special period mainly for one year. This is an important micro economic scale which is a symbol of the economy and efficiency (effect). This is because GDP is associated with many socio-economic parameters such as poverty, unemployment, living standards, education, health level etc. In most cases, this association is based on slight increase or increase.
Quick Links
Gross Domestic Product
India has ranked number 6th in the world in terms of economy, surpassing Britain and France. The American think tank World Population Review has released the 2021 report. According to this, India’s GDP reached the level of $ 2.95 trillion (Rs 295 lakh crore) last year. Britain was fifth with an economy of $ 3.11 trillion and France at number 7 with $ 2.94 trillion. India was ranked number 7 in 2018.
Britain was 5th and France was ranked 6th. In this article you can find complete details for Indian GDP like – How GDP is Measured, Main emphasis of GDP, Current gdp of india 2022, gdp of india 2022, Details for how to calculate gdp of india. Now you can scroll down below and check more details for Gross Domestic Product.
GDP is the best way to understand the economy of any country. GDP stands for gross domestic product. Which is the market value of officially recognized final goods and services produced in a given period. It is also a financial indicator that measures the total production of the country. The production done by every person and industries in the country is also included. Per capita GDP (Capita on GDP) is generally considered to be the life-level of a country and the prosperity index of the economy.
“Gross domestic product (GDP) is the market value of all final goods and services produced within the territory of a country during a given period of time.”
GDP of India 2024
According to the International Monetary Fund, as of January 2024, India’s total GDP (nominal ie at current prices) was $3.942 billion. India’s share in the total GDP of the world is about 3.36 percent. Similarly, India’s real GDP (at constant prices for 2011-12) was Rs 140.78 lakh crore.
| S. No. | Country Name | Continent | GDP (USD Billion)* |
| 1 | United States | America | 28,783 |
| 2 | China | Asia | 18,536 |
| 3 | Germany | Europe | 4,730 |
| 4 | Japan | Asia | 4,112 |
| 5 | India | Asia | 3,942 |
| 6 | United Kingdom | Europe | 3,502 |
| 7 | France | Europe | 3,132 |
| 8 | Brazil | America | 2,333 |
| 9 | Italy | Europe | 2,332 |
| 10 | Canada | America | 2,242 |
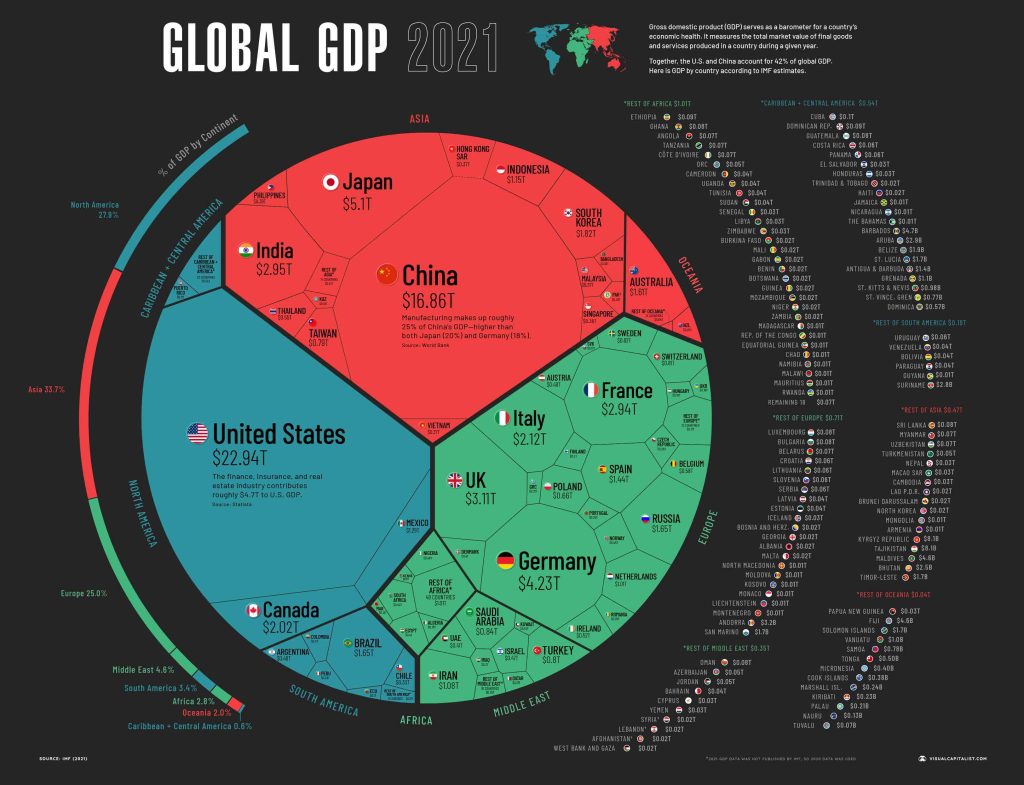
GDP of the country at Rs 394 lakh crore ($3.94 trillion); Government has set a target of 355 lakh crore by 2025
| GDP (PPP) | 2024 estimate |
|---|---|
|
Total
| Rs 394 lakh crore |
|
Per capita
| $8,483 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
|
Total
| $2.94 trillion |
|
Per capita
| $2,198 |
GDP Statistics
| GDP | US$2.454 trillion (nominal; 2017 $9.489 trillion (PPP; 2017)2.6 lakh crores USD (2017) |
|---|---|
| GDP rank | 6th (nominal); 3rd (PPP) |
|
GDP growth
| 7.2% (2017,IMF) |
|
GDP per capita
| $1,850 (nominal est.; 2017) $7,153 (PPP est; 2017) |
|
GDP per capita rank
| 140th (nominal) / 122nd (PPP) |
|
GDP by sector
| Agriculture: 16.5% Industry: 29.8% Services: 45.4% (2016 est.) |
|
Inflation (CPI)
| 1.54% (June 2017) |
|
Base borrowing rate
| 6.50% (as on 23 June 2017) |
|
Population below poverty line
| 12.4% of population below the poverty line of $1.90/day (2011–12, World Bank) |
GDP of Other Countries
| India | 2.95 lakh crores USD (2021) | |
| United States | 22.94 lakh crores USD (2017) | |
| China | United Kingdom | 3.11 lakh crores USD |
| Russia | 1.65 lakh crores USD (2017) |
How to calculate GDP?
GDP in India is calculated quarter-by-quarter. Agriculture, industry and service in India are three important parts, on the basis of which GDP is determined. For this, whatever production is done in the country, as much as personal consumption, the investment in business and the amount of money the government spends within the country are added. Apart from this, the total imports (the things which are sold for foreign countries) are reduced from the total imports (the things which are imported from abroad). The figure that comes up is also added to the expenditure incurred above. This is the GDP of our country.
This equation can be used in calculating GDP.
Gross Domestic Product = Personal Consumption + Gross Investment + Government Investment + Government Expenditure + (Export – Import)
GDP deflator is extremely important because it measures price inflation.
It is calculated by dividing the unreal (nominal) GDP from the actual GDP and multiplied by 100 (on the basis of Formula).
Main emphasis:
1. Market value:
To arrive at the GDP all the goods and services are measured at their market prices. This it enables to bring a standardized measure of valuing the goods and services.
2. Final Goods:
GDP considers final goods and services only. Final goods & services mean those which are readily available for the end user to consume. As we are already including the value of final goods which comes through different forms of intermediary, it is not required to include the intermediary goods again.
For example: If a fisherman sells fishes to dealer at Rs.100 and the same is sold by the dealer to final consumer at Rs. 200. Now as a final product available to consumer, we include the market value of fish at Rs 200. This includes the value of intermediary RS 100 when it is being passed from the fisherman.
3. Goods & Services:
GDP includes the tangible and intangible production made within a nation’s territory. Tangible things are those which can be seen and touched Eg: Mobiles, vehicles, fruits and other goods. In tangible things are those which cannot be seen and touched. Eg : Software services, Advisory & audit service.
4. Produced in the country:
GDP considers only those goods services which are produced within the territory of the country by either the foreigners or Indians. It means goods which are produced outside the territory by Indian producers are not considered to compute GDP.
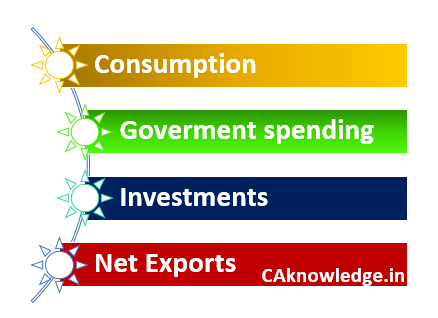
How it is measured:
Generally GDP is measured for a period of an year or a quarter. GDP is measured by using following formula:
GDP = C + I + G + NX
Here
C = Indicates consumption which is very broader in this context. It includes all the spending made on goods and services by the consumers in a nation.
I = Indicates Investment. This means the total amount spent on goods and services which will be used for further production of goods and services. Like investment made on capital equipment, machineries, factory buildings, technology etc.,
G = Indicates total government’s spending on goods and services at different levels of governing the public.
NX = Indicates net amount of exports. i.e., NX=Total exports – total imports.
GDP of India (In Billions)
GDP at Current Prices
| Year | GDP |
| 2014 | $2051.228 |
| 2015 | $2182.577 |
| 2016 | $2384.726 |
GDP based on purchasing-power-parity (PPP) valuation of country GDP
(In Billions)
| Year | GDP |
| 2014 | $7411.09 |
| 2015 | $8027.03 |
| 2016 | $8727.96 |
Source of Data – IMF
Read Relevant Articles
- Interest Rate of NSC, PPF, KYP, SSY, SCSS
- How to get loan against PPF
- Two Best Investments To Double Your Savings
- EPFO Mobile App
- Sectoral Mutual Funds
- Mutual funds Pros and Cons
- Retail Investors and Mutual Funds
- Best Long Term Investment Plans
- KVP, PPF, NSC Which is best?
- National Savings Certificate (NSC