Difference between Main Board IPO and SME IPO: Check complete details about what a Main Board IPO is and what an SME IPO is. Check out the main differences between Main Board (Regular) IPO and SME IPO from below…
Quick Links
Main Board IPO:
Initial Public Offering is the first invitation made by a company to the public to subscribe for its securities. It is the regular IPO that we hear about day to day in the financial dailies. Must read Employees Stock Option Plan (ESOP).
SME IPO:
It is a separate platform designed and implemented by the National Stock Exchange and Bombay Stock Exchange specifically for small and medium enterprises to list their securities on the stock exchange and raise capital from investors.
Key Differences Between Main Board (Regular) IPO and SME IPO:
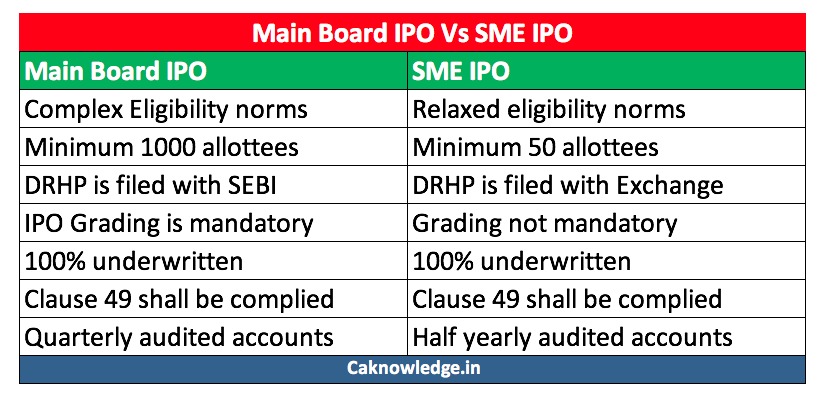
| Parameter | Main Board IPO | Main Board IPO |
|---|---|---|
| Eligibility | The eligibility criteria are slightly more complex than for SMEs to ensure that capable firms are given access to the stock market | Eligibility norms are very relaxed when compared to regular IPO |
| Paid up capital | The face value of the paid-up capital after the issue should be at least Rs 10 crore. | The paid-up capital after the issue should not exceed Rs 25 crore. |
| Minimum number of allottees | There should be at least 1000 allottees | Should be at least 50 allottees |
| IPO Application size | Between Rs.5,000 – Rs.7,000. | At least Rs.1,00,000 |
| Draft Red-herring prospectus – DRHP | In a main board IPO, DRHP is filed with SEBI for vetting | Observations on DRHP are done by the stock exchange itself |
| IPO Grading | Grading of IPO by the rating agencies registered with SEBI is mandatory | Grading is not mandatory |
| Underwriting | Mandatory except in the cases where 50% of the total issue is offered for compulsory subscription by Qualified institutional buyers (QIB) | IPO is underwritten 100% with 15% being on the books of merchant bankers |
| Track record | Three years track record of profitability | Operating cash flows should be positive for the past two years |
| Market making | Post issue, market making is not mandatory | Market making is mandatory to make the securities more liquid |
| Corporate governance | Clause 49 of the listing agreement shall be applicable | Clause 49 of the listing agreement shall be applicable |
| Reporting requirements | Quarterly audited accounts should be submitted | Half-yearly audited accounts should be submitted |
| Focus | Focused on institutional and High-worth individuals | Focused on institutional and High net worth individuals |

