Banks balance sheets contain certain unusual items when compared to others. We shall have an over view of the same. Know more about Important Items of Banks Balance Sheets from below.
Quick Links
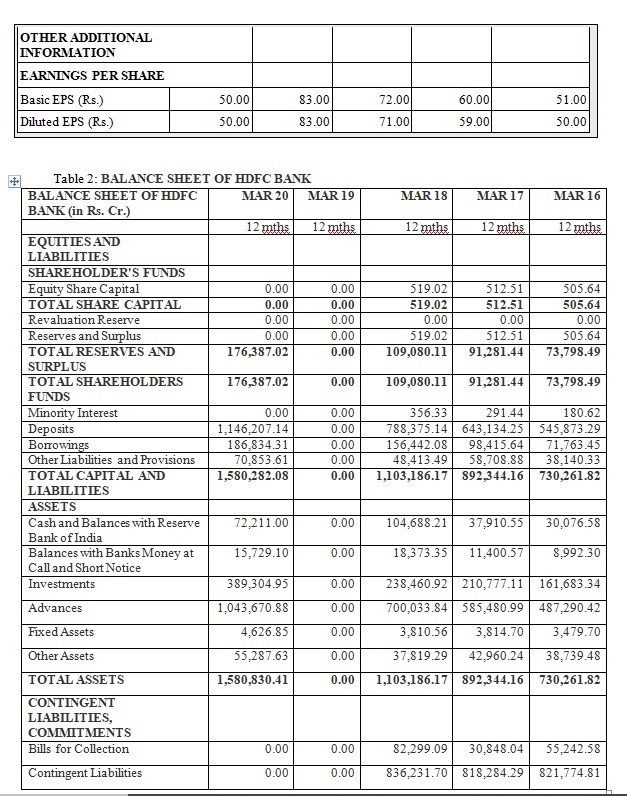
Liabilities Side of Bank Balance Sheet
- Share Capital: Consist of Authorised, Issued, Subscribed and Paid-up share capital are shown separately. Under the head, Paid-up Capital, calls in arrears are reduced and forfeited share amount is added.
- Reserve Fund and others: As under B R Act every bank which is incorporated in India has to transfer twenty percent of its profit before declaring dividend each year to the Reserve Fund.
- Deposits and other accounts: Though it appears as a single head, it consists of Fixed Deposits (which are held for a fixed period), Savings Bank as well as Current Account balances (which are repayable on demand) and others.
Assets Side of Bank Balance Sheet
1. Money at call and short notice:
Money is borrowed by one bank from another usually for a short period of 1 to 14 days for meeting certain commitments. For a bank which lends this money it is an asset in the form of receivable. This type of transaction is known as inter-bank transaction. When banks have surplus funds they lend and when they have shortage they borrow.
Banks also approach RBI and other primary dealers for the same purpose. Banks make use of ‘Repo’ facility for borrowing with RBI. These are included under this head. The interest rates on such borrowings is charged as an expense. Rate of interest will depend on market demand and supply (except in the case of Repo transaction which will be depend on repo rate.)
2. Advances:
The advances consist of Loans, Cash credit and overdraft. Loans are given a fixed period to customer repayable over a period of time by way of EMI or instalments. Cash credit facility is given for a period of one year by way of a hypothecation limit against securities in the form of current assets/ securities. Customers are permitted to draw money up to a limit sanctioned. It is a running account in which deposits will also be made.
In case of Overdraft a customer will be allowed to draw money from current account against some collateral security like insurance policies, shares, NSC and other tangible securities.
3. Bills receivable being Bills for collection as per contra:
Bills are given by customers for collection and subsequent credit to their accounts. Such bills are sent for collection and on realization these are credited to customers’ account. During the year end when bills which remain outstanding for collection banks pass the following entries :
Bills received being bills for collection Dr
To Bills for Collection being bills receivable account.
The first entry indicates the amount receivable and it is taken on the assets side. The second entry denotes amount payable is taken on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. The amounts are identical and known as contra items
4. Acceptances, Endorsements and other obligations:
During the course of their business banks open letters of credit, issue bank guarantee, endorse promissory notes, accept or co-accept bills on behalf of customers. Under such actions a bank is liable to third parties on behalf of customers. In such cases banks obtain counter guarantees to protect themselves in case if liabilities devolve on them. Such counter guarantees represent an asset. For all such outstanding transactions contra entries are passed :
Constituents liability for Acceptances, Endorsements /other obligations Dr
To Acceptances, Endorsements/other obligations.
The former entry is taken in the assets side and the latter is taken on the liabilities side
Non-Banking Assets:
These are non-financial Assets and are tangible. e.g. machinery, equipment, real estate, inventory, vehicles. When a borrower is unable to repay the amount of the loan in cash and as a substitute offers to the bank an asset. This is known as a non-banking asset. This one is provided apart from the asset already given as collateral security to the bank to purchase so as to settle their dues. When these assets are purchased by the banks, they are known as non banking assets.
Banks are required to dispose off those assets within a specified timeframe as mandated by RBI. They also have the responsibility to finally convert these non-cash recoveries in to cash as recoveries. Profit or loss on disposal of such assets are to be disclosed in profit and loss of account of the bank.
Gold and Silver:
Gold appears as a part of assets and appears under the head ‘investments’. Silver appears under “Other assets”.
Locker /Safe Deposit vaults:
These are assets and as such are included under Furniture and fixtures.
Branch Adjustment Account:
In a Bank there are many transactions take place. They may be between Head office and branches vice-versa, between branches. They are properly reconciled at periodical intervals. However at the year-end time there could be outstanding transactions pending reconciliation. Thus there could be a balance in the inter-office.
The inter-office adjustment balance, if in debit, should be shown under this head. Only net position of inter-office accounts inland as well as foreign should be shown here. For arriving at the net balance of inter-office adjustment accounts all connected inter-office accounts should be aggregated and the net balance, if in debit, only should be shown, representing mostly items in transit and unadjusted items. If the balance is in credit it is shown under liabilities side.
Recommended

