All about Account Payee Cheque Vs Crossed Cheque: Difference between Account Payee Cheque and Crossed Cheque. Before we go too much into detail about account payee cheque & crossed cheque, it is important to know what are Negotiable Instruments! So, let us have a look on the definition & characteristics of Negotiable Instrument. check more details regarding “All about Account Payee Cheque Vs Crossed Cheque” from below…..
Quick Links
All about Account Payee Cheque Vs Crossed Cheque
Definition:
The law relating to negotiable instruments is contained in the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881. The term “negotiable instrument” means a document transferable from one person to another. However the Act has not defined the term. It merely says that “A .negotiable instrument” means a promissory note, bill of exchange or cheque payable either to order or to bearer.
Must Read – Callable and non callable fixed deposits
Noteworthy Characteristics of Negotiable Instruments
Following are the important characteristics of negotiable instruments:
- They are freely transferable.
- The holder of the instrument is presumed to be the owner of the property contained in it.
- A holder in due course gets the instrument free from all defects of title of any previous holder.
- The holder in due course is entitled to sue on the instrument in his own name.
- The instrument is transferable till maturity and in case of cheques till it becomes stale (on the expiry of 3 months from the date of issue).
- Certain equal presumptions are applicable to all negotiable instruments unless the contrary is proved.
Negotiable Instruments include Cheques, Promissory Notes, Bills of Exchange, etc.
Must Read – balance enquiry number
Let us go into a detailed study about Cheques.
Features of a Cheque
- It is always payable on demand.
- It is always drawn on a banker.
- It does not require acceptance.
- A cheque can be drawn on the bank where the drawer has an account.
- Cheques may be payable to the drawer himself. It may be made payable to the bearer on demand unlike a bill or a note.
- A cheque is usually valid for three months. However, it is not invalid if it is post dated.
- No Stamp is required to be affixed on cheques.
Must Read – Hypothecation
What is crossing of cheque?
A cheque is either “open” or “crossed”. An open cheque can be presented by the payee to the paying banker and is paid over the counter. A crossed cheque cannot be paid across the counter but must be collected through a banker.
Modes of Crossing
There are two types of crossing which may be used on cheque, namely: (i) General & (ii) Special.
General Crossing: Where a cheque bears across its face, an addition of two parallel transverse lines and/or the addition of the words “and Co.” between them, or addition of “not negotiable”, it is a General Crossing.
Special Crossing: In case of special crossing, the paying banker needs to honour the cheque only when it is prescribed through the bank mentioned in the crossing or it’s agent bank.
| Specimen of a general crossing | Specimen of a special crossing |
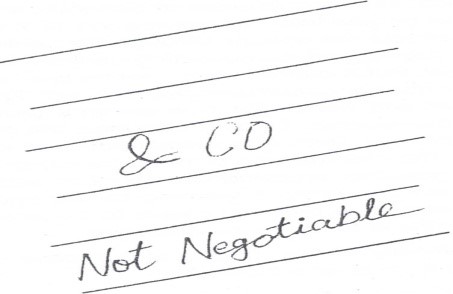 |  |
Account Payee’s Crossing:
Such crossing does, in practice, restrict negotiability of a cheque. It warns the collecting banker that the proceeds are to be credited only to the account of the payee, or the party named on the cheque, or his agent.

Recommended Articles
