Understanding The Process of Debt Securitization, Debt Securitization is a very important topic that is easy to understand but many students generally skip this topic by presuming that it is difficult. As per the oxford advanced learner dictionary, the meaning of the word debt is “a sum of money that somebody owes”, “a situation of owing money, especially when you cannot pay.” Now check more details about “Understanding The Process of Debt Securitization” from below
Quick Links
Understanding The Process of Debt Securitization
What is securitisation?
Securitization refers to pooling debts into homogeneous groups and selling the amount realized from them in the form of securities to investors.
Debt Securitization:
Debt securitization is a method of reusing funds. It is a process where loans are converted and sold in the form of assets. In simple words, prime banking institution issues loans to several intermediaries banks. These banks, also known as special purpose vehicles (SPV), further converts this loan in the form of debt securities and sells it to various other buyers in the form of marketable securities. However, these buyers should be qualified buyers (they are also known as institutional buyers). Debt securitization helps in better balance sheet management.
Friends let me explain this to you with the help of diagram:
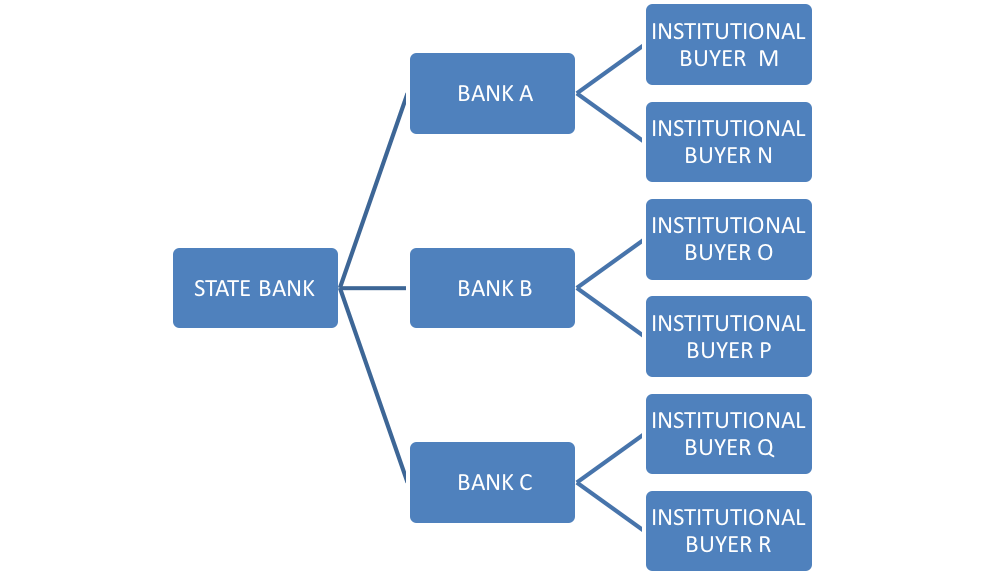
In the above table state bank is performing the function of originator. Bank A, Bank B, Bank C is performing the function of special purpose vehicle. This function is known as pooling function. Institutional buyers are getting marketable securities. Thus, they are also known as qualified institutional buyers.
Friends, it is also necessary to understand the process of debt securitization. So let us have a look on this process:
- First of all, we need to bifurcate the loans into a homogeneous pool, which is, bringing like kind of loans together.
- Which factors to consider for determining similarity between loans is always a question. However, the pool basis may be a rate of interest, degree of risk, maturity pattern, etc.
- After the pool is created it is transferred to the special purpose vehicle. Special purpose vehicle acts as a trustee.
- After the assets are transferred to the trustee, the special purpose vehicles sell the securities to the investors.
- Generally, the SPV will issue securities to different investors so that the probability of losses is reduced.
What are the parties involved in debt securitization?
- Originator: This is the party that initiates the entire debt securitization transaction. It holds the financial assets that need to be securitized.
- Special Purpose Entity (SPE): The party which acquires the asset in debt securitization is known as SPE. It is also responsible for holding the asset till maturity. It acts as a trust and is responsible for converting loans into marketable securities.
- Investor: It is the person who finances the acquisition of securitized assets by subscribing to marketable securities issued by a special purpose entity. These investors generally include institutional investors such as insurance companies and others. However, they need to qualify for acquiring marketable securities.
What are the functions of debt securitization?
The origination function: Let us suppose I am a banking company and I am giving some loan to a borrower. Of course, the loan will be given by me for some consideration, say, some asset. Thus, I will record an asset in my books. The financial asset that comes into existence is known as the origination function.
The pooling function: Different loans are converted into homogenous groups and are transferred in favor of special purpose vehicles. This special purpose vehicle acts as a trustee. This pooling of assets in favor of special purpose vehicle is known as pooling function.
The securitization function: Once the assets are transferred in favor of a special purpose vehicles, then the SPV issues its securities to the different qualified buyers. This function of issuing securities to qualified institutional buyers is known as the securitization function.
Recommended Articles

